Stereophotogrammetry method for 3D content creation
Another unique method for digitizing and reconstructing real-world three-dimensional objects is stereophotogrammetry. Stereophotogrammetry is a digitization technique where two-dimensional (2D) images (photos) or video frames are used to recreate a digital, three-dimensional (3D) model of a real object. The 3D model generated using this method is an accurate digital replica of the real object, which can be utilized for measurements, reconstructions, modeling, and integration into virtual solutions.
To achieve the most precise 3D model using the stereophotogrammetry method, it is recommended to use no fewer than twenty images or frames captured from all sides of the object of interest. Each new photo or video frame should overlap with two-thirds of the previous image to ensure pixel continuity and overlap, which is crucial for accurate vector and position calculations during the object reconstruction process (see Fig. 1).
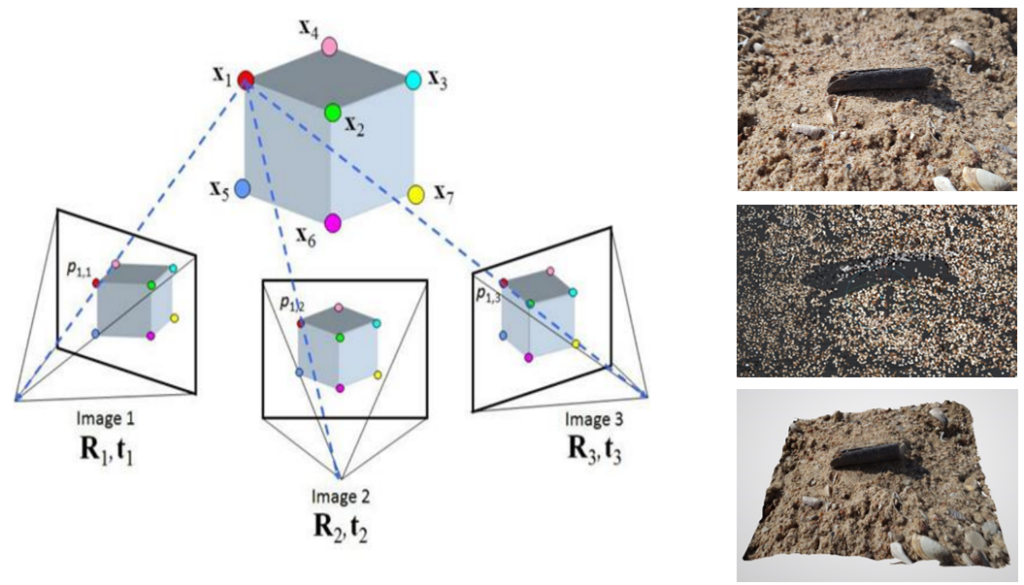
The principle of the stereophotogrammetry and photogrammetry method is based on extracting spatial information about photographed objects from digital image data. This process includes the following stages:
- Image acquisition. Capturing multiple high-quality images of the object from different angles. For stereophotogrammetry, images must overlap sufficiently (at least two-thirds) to ensure accurate reconstruction.
- Image alignment. Matching common features across overlapping images to determine their relative positions and orientations in 3D space. This step is crucial for creating a coherent spatial framework.
- Point cloud generation. Identifying and triangulating corresponding points across the images to create a dense point cloud representing the object’s surface geometry. This process is based on trigonometry, enabling the precise reconstruction of the object’s geometry.
- Mesh construction and texture mapping: Converting the point cloud into a 3D mesh, which provides a structured representation of the object’s surface. After creating 3D mesh, the textures from the original images are applied onto the 3D model to enhance realism and visual fidelity.
The stereophotogrammetry methodology allows for the precise determination of object shapes and positions in an environment, similar to how the human visual system functions.
Stereophotogrammetry is widely used in cartography, architecture, archaeology, forensic science, medicine, and other fields where accurate spatial information about objects is essential. It is employed to reconstruct three-dimensional models of objects, collect and store precise object data in the form of digital 3D models.
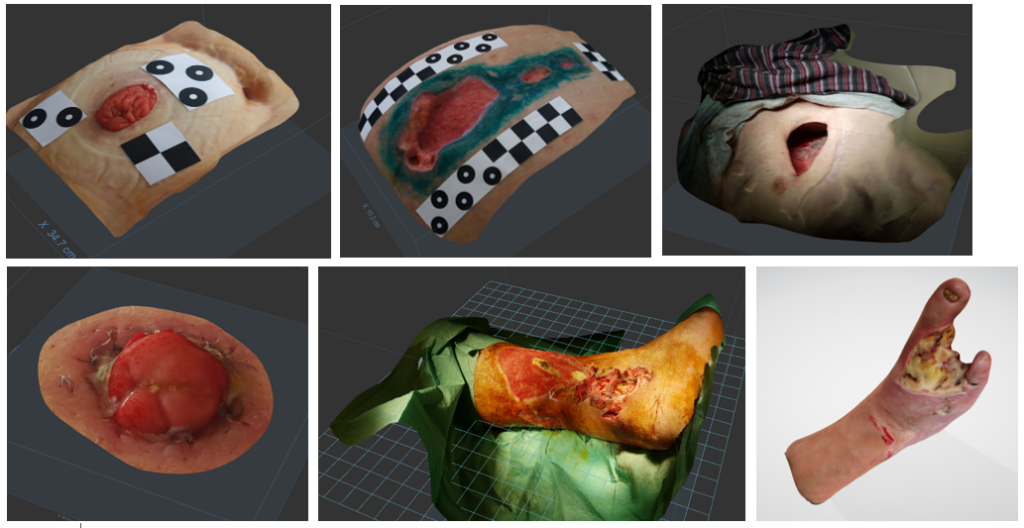
See the examples of captured 3D models, using this methos, that are used in surgical trainings.
Sources:
[1] https://www.sut.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/011-Stereophotogrammetry-M-Sayer-Tritonia-Scientific.pdf